LC239 Sliding Window Maximum
Problem
Given an array nums, there is a sliding window of size k which is moving from the very left of the array to the very right. You can only see the k numbers in the window. Each time the sliding window moves right by one position. Return the max sliding window.
Follow up:
Could you solve it in linear time?Example:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
Output: [3,3,5,5,6,7]
Explanation:
Window position Max
--------------- -----
[1 3 -1] -3 5 3 6 7 3
1 [3 -1 -3] 5 3 6 7 3
1 3 [-1 -3 5] 3 6 7 5
1 3 -1 [-3 5 3] 6 7 5
1 3 -1 -3 [5 3 6] 7 6
1 3 -1 -3 5 [3 6 7] 7Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 10^5-10^4 <= nums[i] <= 10^41 <= k <= nums.length
Think
首先将整个数组按k个一组,分成多个block,设left[i]表示从当前block的左端到当前位置的最大值,right[i]表示从当前block的右端到当前位置的最大值,对于每一个windows [i, i + k - 1]来说,windows内的最大值就是left[i + k - 1]和right[i]中的较大值。
Code
1 | vector<int> maxSlidingWindow(vector<int>& nums, int k) { |
LC424 Longest Repeating Character Replacement
Problem
Given a string
sthat consists of only uppercase English letters, you can perform at mostkoperations on that string.In one operation, you can choose any character of the string and change it to any other uppercase English character.
Find the length of the longest sub-string containing all repeating letters you can get after performing the above operations.
Note:
Both the string’s length and k will not exceed 104.Example 1:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
s = "ABAB", k = 2
Output:
4
Explanation:
Replace the two 'A's with two 'B's or vice versa.Example 2:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
s = "AABABBA", k = 1
Output:
4
Explanation:
Replace the one 'A' in the middle with 'B' and form "AABBBBA".
The substring "BBBB" has the longest repeating letters, which is 4.
Think
窗口为[left, right],右移一位right,取得此时的最大count,然后将多余的左边的字符删去,右移left,比较此时的长度值。
p.s. 这里不需要关注maxCount对应的字符是哪一个,maxCount可能在某一次的序列中是invalid的,但是这个maxCount在之前某一次的子串中是符合要求的,因此并不需要将maxCount变小。
Code
1 | int characterReplacement(string s, int k) { |
LC480 Sliding Window Median
Problem
Median is the middle value in an ordered integer list. If the size of the list is even, there is no middle value. So the median is the mean of the two middle value.
Examples:
2
[2,3]`, the median is `(2 + 3) / 2 = 2.5Given an array nums, there is a sliding window of size k which is moving from the very left of the array to the very right. You can only see the k numbers in the window. Each time the sliding window moves right by one position. Your job is to output the median array for each window in the original array.
For example,
Given nums =[1,3,-1,-3,5,3,6,7], and k = 3.
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
--------------- -----
[1 3 -1] -3 5 3 6 7 1
1 [3 -1 -3] 5 3 6 7 -1
1 3 [-1 -3 5] 3 6 7 -1
1 3 -1 [-3 5 3] 6 7 3
1 3 -1 -3 [5 3 6] 7 5
1 3 -1 -3 5 [3 6 7] 6Therefore, return the median sliding window as
[1,-1,-1,3,5,6].Note:
You may assumekis always valid, ie:kis always smaller than input array’s size for non-empty array.
Answers within10^-5of the actual value will be accepted as correct.
Think
- Approach 1
Two Heap,使用一个最大堆lo和一个最小堆hi,始终保持两者的平衡,即lo的大小要么等于hi要么比hi大1;删除元素的时候并不真的删除,而是先存入hash map中,最后将两个堆中所有顶端元素为待删除元素的pop出去
- Approach 2
multiset,有序,使用mid表示当前窗口的中间下标。每次插入新数字的时候,如果新插入的数字比中间值大或者相等,则mid不变,如果比中间值小,则mid–;删除旧数字的时候,如果旧数字比中间值大,则mid不变,否则mid++。
p.s. 这里是否包含等于号的原因在于C++在插入同值的数字进multiset的时候会优先插在尾端,所以对于相等的情况,插入并不会改变mid在[k / 2]的位置;而在删除的时候,由于我们是删除第一个等于这个值的数字,这就会导致mid变成[k / 2] - 1,因此对于相等的情况,mid需要自增1。
Code
- Approach 1
1 | vector<double> medianSlidingWindow(vector<int>& nums, int k) { |
- Approach 2
1 | vector<double> medianSlidingWindow(vector<int>& nums, int k) { |
LC567 Permutation in String
Problem
Given two strings s1 and s2, write a function to return true if s2 contains the permutation of s1. In other words, one of the first string’s permutations is the substring of the second string.
Example 1:
2
3
Output: True
Explanation: s2 contains one permutation of s1 ("ba").Example 2:
2
Output: FalseConstraints:
- The input strings only contain lower case letters.
- The length of both given strings is in range [1, 10,000].
Think
用int数组当作map存储当前m长度下的每个字符的数目,每次滑动窗口的时候,判断此时是否产生的新的匹配字符数或者已经匹配好的字符数被取消。
Code
1 | bool checkInclusion(string s1, string s2) { |
LC1020 Number of Enclaves
Problem
Given a 2D array
A, each cell is 0 (representing sea) or 1 (representing land)A move consists of walking from one land square 4-directionally to another land square, or off the boundary of the grid.
Return the number of land squares in the grid for which we cannot walk off the boundary of the grid in any number of moves.
Example 1:
2
3
4
Output: 3
Explanation:
There are three 1s that are enclosed by 0s, and one 1 that isn't enclosed because its on the boundary.Example 2:
2
3
4
Output: 0
Explanation:
All 1s are either on the boundary or can reach the boundary.
Think
BFS
Code
1 | int numEnclaves(vector<vector<int>>& A) { |
LC1034 Coloring A Border
Problem
Given a 2-dimensional
gridof integers, each value in the grid represents the color of the grid square at that location.Two squares belong to the same connected component if and only if they have the same color and are next to each other in any of the 4 directions.
The border of a connected component is all the squares in the connected component that are either 4-directionally adjacent to a square not in the component, or on the boundary of the grid (the first or last row or column).
Given a square at location
(r0, c0)in the grid and acolor, color the border of the connected component of that square with the givencolor, and return the finalgrid.Example 1:
2
Output: [[3, 3], [3, 2]]Example 2:
2
Output: [[1, 3, 3], [2, 3, 3]]Example 3:
2
Output: [[2, 2, 2], [2, 1, 2], [2, 2, 2]]Note:
1 <= grid.length <= 501 <= grid[0].length <= 501 <= grid[i][j] <= 10000 <= r0 < grid.length0 <= c0 < grid[0].length1 <= color <= 1000
Think
BFS,向四个方向遍历,只要有一个方向是数组边界或者不是给定的颜色,则说明当前点是border,不需要再向外扩展了。
Code
1 | vector<vector<int>> colorBorder(vector<vector<int>>& grid, int r0, int c0, int color) { |
LC1037 Valid Boomerang
Problem
A boomerang is a set of 3 points that are all distinct and not in a straight line.
Given a list of three points in the plane, return whether these points are a boomerang.
Example 1:
2
Output: trueExample 2:
2
Output: falseNote:
points.length == 3points[i].length == 20 <= points[i][j] <= 100
Think
斜率计算
Code
1 | bool isBoomerang(vector<vector<int>>& points) { |
LC1138 Alphabet Board Path
Problem
On an alphabet board, we start at position
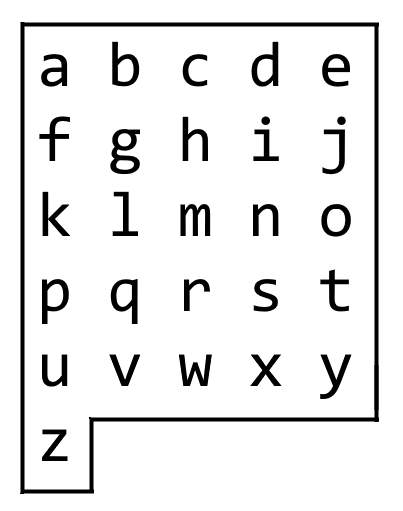
(0, 0), corresponding to characterboard[0][0].Here,
board = ["abcde", "fghij", "klmno", "pqrst", "uvwxy", "z"], as shown in the diagram below.
We may make the following moves:
'U'moves our position up one row, if the position exists on the board;'D'moves our position down one row, if the position exists on the board;'L'moves our position left one column, if the position exists on the board;'R'moves our position right one column, if the position exists on the board;'!'adds the characterboard[r][c]at our current position(r, c)to the answer.(Here, the only positions that exist on the board are positions with letters on them.)
Return a sequence of moves that makes our answer equal to
targetin the minimum number of moves. You may return any path that does so.Example 1:
2
Output: "DDR!UURRR!!DDD!"Example 2:
2
Output: "RR!DDRR!UUL!R!"Constraints:
1 <= target.length <= 100targetconsists only of English lowercase letters.
Think
求出两个字母的垂直距离和水平距离,根据距离加UDLR即可
Code
1 | string alphabetBoardPath(string target) { |
LC1145 Binary Tree Coloring Game
Problem
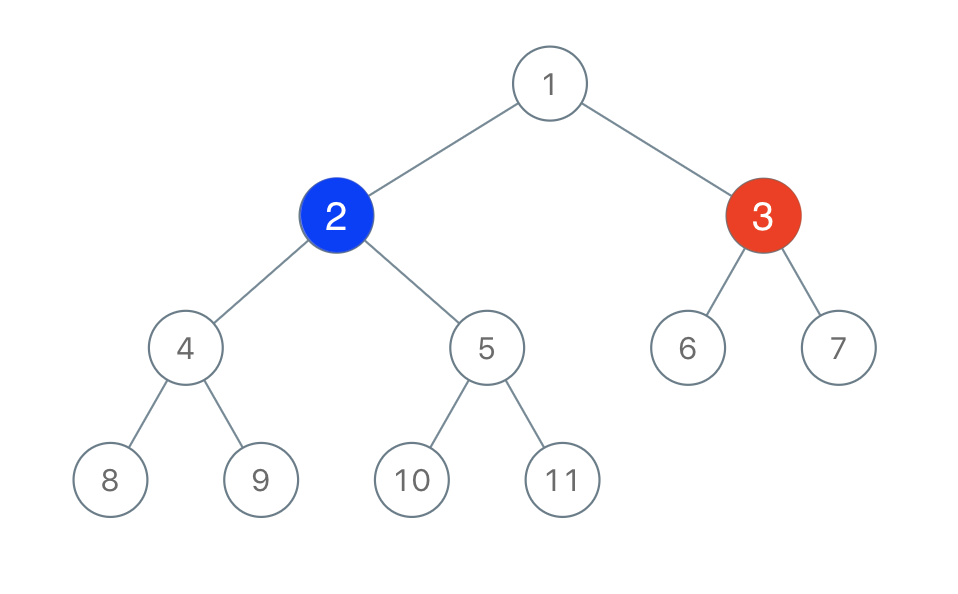
Two players play a turn based game on a binary tree. We are given the
rootof this binary tree, and the number of nodesnin the tree.nis odd, and each node has a distinct value from1ton.Initially, the first player names a value
xwith1 <= x <= n, and the second player names a valueywith1 <= y <= nandy != x. The first player colors the node with valuexred, and the second player colors the node with valueyblue.Then, the players take turns starting with the first player. In each turn, that player chooses a node of their color (red if player 1, blue if player 2) and colors an uncolored neighbor of the chosen node (either the left child, right child, or parent of the chosen node.)
If (and only if) a player cannot choose such a node in this way, they must pass their turn. If both players pass their turn, the game ends, and the winner is the player that colored more nodes.
You are the second player. If it is possible to choose such a
yto ensure you win the game, returntrue. If it is not possible, returnfalse.Example 1:
2
3
Output: true
Explanation: The second player can choose the node with value 2.Constraints:
rootis the root of a binary tree withnnodes and distinct node values from1ton.nis odd.1 <= x <= n <= 100
Think
使用一个helper函数遍历数组,同时返回以当前节点为根节点的子树的元素数目。要选择y使得蓝色节点最大化,则y可选的主要有三个:
- x的左子节点
- x的右子节点
- x的父节点
对于左右子节点,我们可以分别用全局变量l和r来记录,对于父节点,则蓝色节点的最大数目为n - l - r,最后判断三者中的最大的那一个是否比n / 2大即可。
Code
1 | int l = -1, r = -1; |
Review
滑动窗口问题主要分为两类:
- 定长窗口,一般使用hash表记录每一个元素的出现次数,然后用新窗口内元素的出现次数和原始的进行比较即可,注意要判断两次,一次是新加入的元素匹配从而导致的元素匹配数+1,或者导致元素不匹配从而匹配的元素数目-1;一次是去除元素之后恰好符合匹配元素的数目从而导致的元素匹配数+1,或者导致元素的匹配数-1。
- 不定长窗口,一般也需要用hash表记录窗口内每一个元素出现的次数,同时需要用while循环将所有不满足要求的left元素从 窗口中移除。