LC125 Valid Palindrome
Problem
Given a string, determine if it is a palindrome, considering only alphanumeric characters and ignoring cases.
Note: For the purpose of this problem, we define empty string as valid palindrome.
Example 1:
1 2 Input: "A man, a plan, a canal: Panama" Output: true
Example 2:
1 2 Input: "race a car" Output: false
Think
双指针,比较两个指针处的char值即可
Code
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 bool isPalindrome (string s) int n = s.size (); int l = 0 , r = n - 1 ; while (l < r){ char cl = change(s[l]); if (cl == '#' ){ l++; continue ; } char cr = change(s[r]); if (cr == '#' ){ r--; continue ; } if (cl != cr) return false ; l++; r--; } return true ; } char change (char c) if (c >= 'A' && c <= 'Z' ){ return (char )(c - 'A' + 'a' ); } else if ((c >= 'a' && c <= 'z' ) || (c >= '0' && c <= '9' )){ return c; } else { return '#' ; } }
LC214 Shortest Palindrome
Problem
Given a string s
Example 1:
1 2 Input: "aacecaaa" Output: "aaacecaaa"
Example 2:
1 2 Input: "abcd" Output: "dcbabcd"
Think
利用KMP算法中的部分匹配表的算法
Code
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 string shortestPalindrome (string s) int n = s.size (); string revStr = s; reverse(revStr.begin (), revStr.end ()); string newStr = s + "#" + revStr; int newN = 2 * n + 1 ; vector <int > f (newN, 0 ) for (int i = 1 ; i < newN; i++){ int t = f[i - 1 ]; while (t > 0 && newStr[i] != newStr[t]){ t = f[t - 1 ]; } if (newStr[i] == newStr[t]){ t++; } f[i] = t; } return revStr.substr(0 , n - f.back()) + s; }
LC409 Longest Palindrome
Problem
Given a string which consists of lowercase or uppercase letters, find the length of the longest palindromes that can be built with those letters.
This is case sensitive, for example "Aa" is not considered a palindrome here.
Note:
Example:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Input: "abccccdd" Output: 7 Explanation: One longest palindrome that can be built is "dccaccd", whose length is 7.
Think
统计所有52个字母出现的次数,累计所有次数 / 2 = k,然后判断是否有奇数出现次数的字母,如果有则返回2 * ,否则返回2 * k + 1。
Code
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 int longestPalindrome (string s) vector <int > m (52 , 0 ) for (auto c: s){ if (c >= 'a' && c <= 'z' ){ m[c - 'a' ]++; } else if (c >= 'A' && c <= 'Z' ){ m[c - 'A' + 26 ]++; } } int res = 0 , flag = false ; for (int i = 0 ; i < 52 ; i++){ res += m[i] / 2 ; if (m[i] % 2 == 1 ){ flag = true ; } } return flag ? 2 * res + 1 : 2 * res; }
LC131 Palindrome Partitioning
Problem
Given a string s , partition s such that every substring of the partition is a palindrome.
Return all possible palindrome partitioning of s .
Example:
1 2 3 4 5 6 Input: "aab" Output: [ ["aa","b"], ["a","a","b"] ]
Think
DFS或者backtracing
Code
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 vector <vector <string >> partition (string s) vector <vector <string >> res; helper(s, 0 , {}, res); return res; } void helper (string s, int start, vector <string > partition, vector <vector <string >>& res) int n = s.size (); if (start == n){ res.push_back(partition); } for (int i = start; i < n; i++){ string str = s.substr(start, i - start + 1 ); if (isP(str)){ partition.push_back(str); helper(s, i + 1 , partition, res); partition.pop_back(); } } } bool isP (string s) string rev = s; reverse(rev.begin (), rev.end ()); return s == rev; }
LC132 Palindrome Partitioning II
Problem
Given a string s , partition s such that every substring of the partition is a palindrome.
Return the minimum cuts needed for a palindrome partitioning of s .
Example:
1 2 3 Input: "aab" Output: 1 Explanation: The palindrome partitioning ["aa","b"] could be produced using 1 cut.
Think
DP,设置两个dp数组
dp[i, j]表示s[i, j]是否为回文串,res[i]表示s[i, n - 1]所需要的最小的cut数目;
for i = n - 1 to 0,我们可以知道res[i]最大为n - i - 1,也就是每个字符都切割开来;
因此接下来需要判断往后的所有s[i, j]是否为回文串,如果为回文串,则res[i] = min(res[j + 1] + 1) (注意这里需要判断j是否已经到达最后一个字符,如果已经到达,则不需要切割,即res[i] = 0)。
Code
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 int minCut (string s) if (s.empty()) return 0 ; int n = s.size (); vector <vector <bool >> dp (n, vector <bool >(n, false )) vector <int > res (n, 0 ) for (int i = n - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--){ res[i] = n - i - 1 ; for (int j = i; j < n; j++){ if (s[i] == s[j] && (j - i < 2 || dp[i + 1 ][j - 1 ])){ dp[i][j] = true ; if (j == n - 1 ){ res[i] = 0 ; } else { res[i] = min (res[i], res[j + 1 ] + 1 ); } } } } return res[0 ]; }
LC9 Palindrome Number
Problem
Determine whether an integer is a palindrome. An integer is a palindrome when it reads the same backward as forward.
Example 1:
Example 2:
1 2 3 Input: -121 Output: false Explanation: From left to right, it reads -121. From right to left, it becomes 121-. Therefore it is not a palindrome.
Example 3:
1 2 3 Input: 10 Output: false Explanation: Reads 01 from right to left. Therefore it is not a palindrome.
Follow up:
Coud you solve it without converting the integer to a string?
Think
解析出每一位数字,然后组合成倒装的数字再判断即可。
Code
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 bool isPalindrome (int x) if (x == 0 ) return true ; if (x < 0 || x % 10 == 0 ) return false ; long rev = 0 ; int pre = x; while (x > 0 ){ rev = rev * 10 + x % 10 ; x = x / 10 ; } return pre == (int )rev; }
LC680 Valid Palindrome II
Problem
Given a non-empty string s, you may delete at most one character. Judge whether you can make it a palindrome.
Example 1:
1 2 Input: "aba" Output: True
Example 2:
1 2 3 Input: "abca" Output: True Explanation: You could delete the character 'c'.
Note:
The string will only contain lowercase characters a-z. The maximum length of the string is 50000.
Think
贪心算法 + 双指针,一个从左边,一个从右边,当找到第一个不同的字符的时候,判断删掉左边或者右边的字符之后剩下的是不是回文串。
Code
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 bool validPalindrome (string s) int n = s.size (); int i = 0 ; while (i < n / 2 ){ if (s[i] != s[n - 1 - i]){ return isP(s, i, n - 2 - i) || isP(s, i + 1 , n - 1 - i); } i++; } return true ; } bool isP (string s, int left, int right) while (left < right){ if (s[left++] != s[right--]){ return false ; } } return true ; }
LC234 Palindrome Linked List
Problem
Given a singly linked list, determine if it is a palindrome.
Example 1:
1 2 Input: 1->2 Output: false
Example 2:
1 2 Input: 1->2->2->1 Output: true
Follow up:
Think
首先通过快慢指针找到中间点,如果是奇数个(2k+1),则令指针指向第k+1个;如果是偶数个(2k),也令指针指向第k+1个;
然后将后半段链表翻转,再比较这两段链表前面的公共部分是否相同即可。
Code
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 bool isPalindrome (ListNode* head) ListNode* secondHalfHead = second(head); ListNode* rev = reverse(secondHalfHead); ListNode* n1 = head, *n2 = rev; while (n1 && n2){ if (n1->val != n2->val){ return false ; } n1 = n1->next; n2 = n2->next; } return true ; } ListNode* reverse (ListNode* head) { ListNode* pre = NULL ; ListNode* cur = head; while (cur){ ListNode* node = cur->next; cur->next = pre; pre = cur; cur = node; } return pre; } ListNode* second (ListNode* head) { ListNode* fast = head, *slow = head; while (fast && fast->next){ slow = slow->next; fast = fast->next->next; } return slow; }
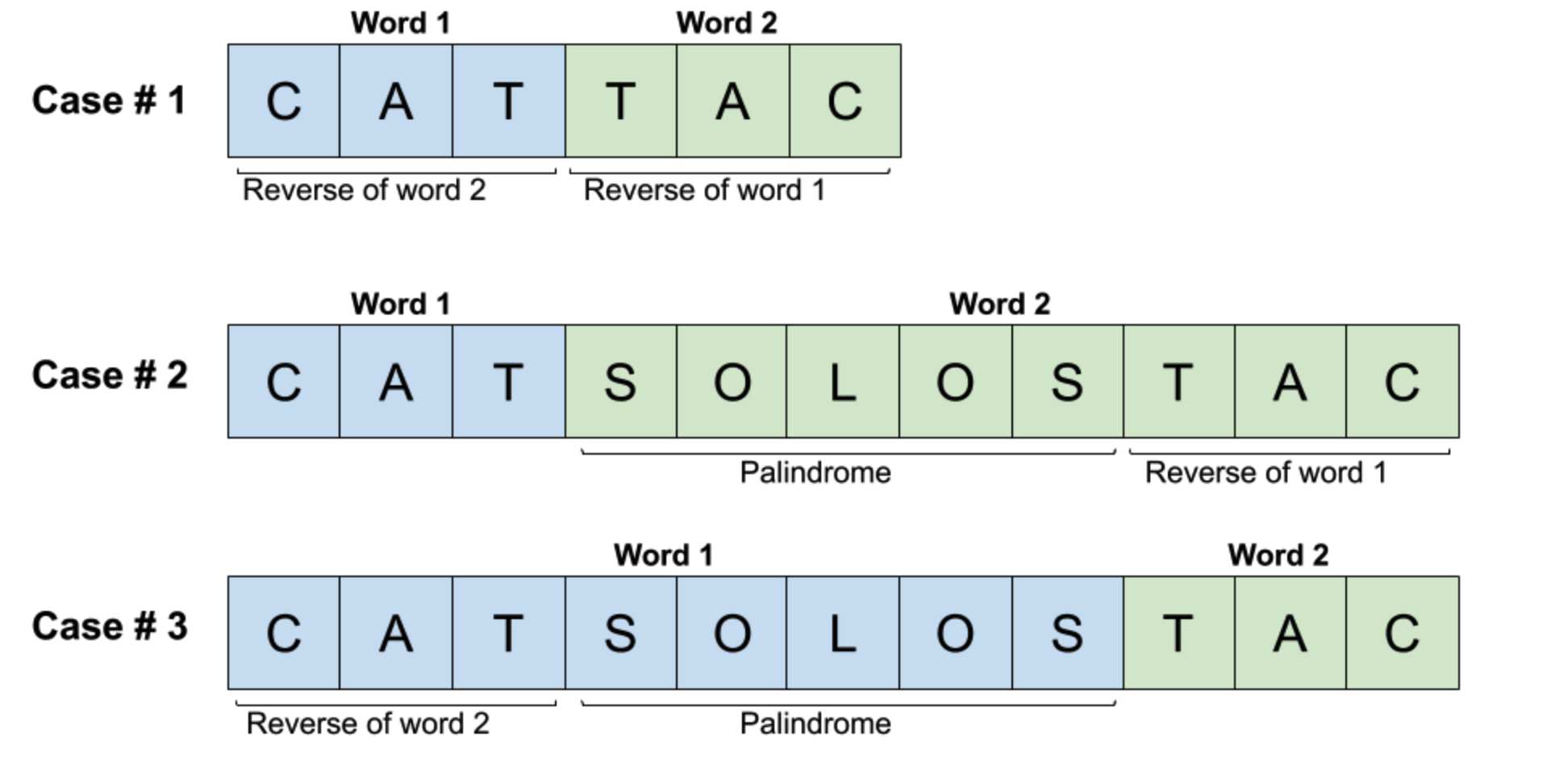
LC336 Palindrome Pairs
Problem
Given a list of unique words, find all pairs of distinct indices (i, j) in the given list, so that the concatenation of the two words, i.e. words[i] + words[j] is a palindrome.
Example 1:
1 2 3 Input: ["abcd","dcba","lls","s","sssll"] Output: [[0,1],[1,0],[3,2],[2,4]] Explanation: The palindromes are ["dcbaabcd","abcddcba","slls","llssssll"]
Example 2:
1 2 3 Input: ["bat","tab","cat"] Output: [[0,1],[1,0]] Explanation: The palindromes are ["battab","tabbat"]
Think
分三种情况,设一组匹配的word为word1和word2
word1和word2一样长
word1比word2长
word1比word2短
前缀树,每一个前缀树的节点包括三部分:
当前节点是哪一个word的结束字符,如果不是结束字符,则赋-1;
当前节点的所有子节点,根据读到不同的字符来判断,因此需要一个hash表;
如果当前节点之后的剩余字符可以组成一个回文串,则将该回文串加上原有字符组成的word的id存储起来
构建前缀树的时候,需要注意,对每一个word,首先遍历word,将每一个字符挂载在树上,同时判断该word的剩余部分是不是回文串,如果是,则将id也挂载在当前节点的第三部分;最后将id放在最后一个节点的第一部分。
在判断的时候,首先确定其中一个word,也就是word1,去找word2。
在三种case中,case3的word2最短,case1其次,case2最长,因此按照case 3 1 2的顺序来判断即可。
Case3 -> 当前读到字符是某一个单词的结尾字符,且word1的剩余字符是回文串
Case1 -> 当前读到的字符是某一个单词的结尾字符,且和word1不是同一个字符
Case2 -> 直接将word1的id和当前节点的第三部分中的所有值组合,放入res中。
还是分三种情况:
Case1: word和reversedWord都在words中,直接返回两个id就可以;
对于case 2和case 3,设定当前遍历到的word为长的那一个。
Case2: 即当前word为word2,则应当有word2的某一个后缀等于word1的翻转,且word2的剩余部分为回文串,因此只需要遍历所有可能的后缀即可;
Case3: 即当前word为word1,则应当有word1的某一个前缀等于word2的翻转,且word1的剩余部分为回文串,因此只需要遍历所有可能的前缀即可。
Code
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 class TrieNode {public : int wordEnding = -1 ; unordered_map <char , TrieNode*> next; vector <int > palindromePrefixRemaining; }; class Solution {public : bool isPalindromeRemaining (string s, int j) int left = j; int right = s.size () - 1 ; while (left < right){ if (s[left] != s[right]){ return false ; } left++; right--; } return true ; } vector <vector <int >> palindromePairs (vector <string >& words) TrieNode *trie = new TrieNode(); for (int i = 0 ; i < words.size (); i++){ string word = words[i]; string revWord = word ; reverse(revWord.begin (), revWord.end ()); TrieNode* cur = trie; for (int j = 0 ; j < word .size (); j++){ if (isPalindromeRemaining(revWord, j)){ cur->palindromePrefixRemaining.push_back(i); } char c = revWord[j]; if (!cur->next.count(c)){ cur->next[c] = new TrieNode(); } cur = cur->next[c]; } cur->wordEnding = i; } vector <vector <int >> res; for (int i = 0 ; i < words.size (); i++){ string word = words[i]; TrieNode* cur = trie; for (int j = 0 ; j < word .size (); j++){ if (cur->wordEnding != -1 && isPalindromeRemaining(word , j)){ res.push_back({i, cur->wordEnding}); } cur = cur->next[word [j]]; if (!cur) break ; } if (!cur) continue ; if (cur->wordEnding != -1 && cur->wordEnding != i){ res.push_back({i, cur->wordEnding}); } for (int id: cur->palindromePrefixRemaining){ res.push_back({i, id}); } } return res; } };
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 bool isPalindrome (string s, int i, int j) int left = i; int right = j; while (left < right){ if (s[left] != s[right]){ return false ; } left++; right--; } return true ; } vector <string > allValidPrefixes (string s) int n = s.size (); vector <string > res; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++){ if (isPalindrome(s, i, n - 1 )){ res.push_back(s.substr(0 , i)); } } return res; } vector <string > allValidSuffixes (string s) int n = s.size (); vector <string > res; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++){ if (isPalindrome(s, 0 , i)){ res.push_back(s.substr(i + 1 )); } } return res; } vector <vector <int >> palindromePairs (vector <string >& words) unordered_map <string , int > map ; for (int i = 0 ; i < words.size (); i++){ map [words[i]] = i; } vector <vector <int >> res; for (string word : words){ int index = map [word ]; string rev = word ; reverse(rev.begin (), rev.end ()); if (map .count(rev) && map [rev] != index){ res.push_back({index, map [rev]}); } for (string suffix: allValidSuffixes(word )){ reverse(suffix.begin (), suffix.end ()); if (map .count(suffix)){ res.push_back({map [suffix], index}); } } for (string prefix: allValidPrefixes(word )){ reverse(prefix.begin (), prefix.end ()); if (map .count(prefix)){ res.push_back({index, map [prefix]}); } } } return res; }
LC479 Largest Palindrome Product
Problem
Find the largest palindrome made from the product of two n-digit numbers.
Since the result could be very large, you should return the largest palindrome mod 1337.
Example:
1 2 3 Input: 2 Output: 987 Explanation: 99 x 91 = 9009, 9009 % 1337 = 987
Note:
The range of n is [1,8].
Think
两个n位的数字相乘,最大为2n位,所以可以先构造出可能为结果的数字,然后判断这个数字是否可以分解成两个n位的数字相乘。
Code
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 int largestPalindrome (int n) if (n == 1 ) return 9 ; int upper = pow (10 , n) - 1 ; int lower = pow (10 , n - 1 ); for (int i = upper; i >= lower; i--){ long cand = buildP(i); for (long j = upper; j * j >= cand; j--){ if (cand % j == 0 && cand / j <= upper){ return cand % 1337 ; } } } return -1 ; } long buildP (int i) string s = to_string(i); reverse(s.begin (), s.end ()); return stol(to_string(i) + s); }
LC516 Longest Palindromic Subsequence
Problem
Given a string s, find the longest palindromic subsequence’s length in s. You may assume that the maximum length of s is 1000.
Example 1:
Output:
One possible longest palindromic subsequence is “bbbb”.
Example 2:
Output:
One possible longest palindromic subsequence is “bb”.
Think
DP,dp[i, j]表示s[i, j]的最长回文子序列,所以有:
d p [ i , j ] = { 1 , i = = j d p [ i + 1 ] [ j − 1 ] + 2 , s [ i ] = = s [ j ] m a x ( d p [ i ] [ j − 1 ] , d p [ i + 1 ] [ j ] ) , o t h e r w i s e dp[i, j] = \begin{cases}1, i==j\\dp[i+1][j-1]+2, s[i] == s[j]\\max(dp[i][j-1], dp[i+1][j]),otherwise\end{cases} d p [ i , j ] = ⎩ ⎪ ⎨ ⎪ ⎧ 1 , i = = j d p [ i + 1 ] [ j − 1 ] + 2 , s [ i ] = = s [ j ] m a x ( d p [ i ] [ j − 1 ] , d p [ i + 1 ] [ j ] ) , o t h e r w i s e
Code
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 int longestPalindromeSubseq (string s) int n = s.size (); vector <int > dp (n, 0 ) int pre = 0 ; for (int i = n - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--){ for (int j = i; j < n; j++){ int tmp = pre; pre = dp[j]; if (i == j) dp[j] = 1 ; else if (s[i] == s[j]){ dp[j] = tmp + 2 ; } else { dp[j] = max (dp[j], dp[j - 1 ]); } } } return dp[n - 1 ]; }
LC647 Palindromic Substrings
Problem
Given a string, your task is to count how many palindromic substrings in this string.
The substrings with different start indexes or end indexes are counted as different substrings even they consist of same characters.
Example 1:
1 2 3 Input: "abc" Output: 3 Explanation: Three palindromic strings: "a", "b", "c".
Example 2:
1 2 3 Input: "aaa" Output: 6 Explanation: Six palindromic strings: "a", "a", "a", "aa", "aa", "aaa".
Note:
The input string length won’t exceed 1000.
Think
中心扩展法,首先确定一个中心,然后同时向左右扩展到最大,这样的中心有2n - 1个
Code
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 int countSubstrings (string s) int n = s.size (); int res = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < 2 * n - 1 ; i++){ int left = i / 2 ; int right = left + i % 2 ; while (left >= 0 && right < n && s[left] == s[right]){ res++; left--; right++; } } return res; }
LC730 Count Different Palindromic Subsequences
Problem
Given a string S, find the number of different non-empty palindromic subsequences in S, and return that number modulo 10^9 + 7.
A subsequence of a string S is obtained by deleting 0 or more characters from S.
A sequence is palindromic if it is equal to the sequence reversed.
Two sequences A_1, A_2, ... and B_1, B_2, ... are different if there is some i for which A_i != B_i.
Example 1:
1 2 3 4 5 6 Input: S = 'bccb' Output: 6 Explanation: The 6 different non-empty palindromic subsequences are 'b', 'c', 'bb', 'cc', 'bcb', 'bccb'. Note that 'bcb' is counted only once, even though it occurs twice.
Example 2:
1 2 3 4 5 Input: S = 'abcdabcdabcdabcdabcdabcdabcdabcddcbadcbadcbadcbadcbadcbadcbadcba' Output: 104860361 Explanation: There are 3104860382 different non-empty palindromic subsequences, which is 104860361 modulo 10^9 + 7.
Note:
The length of S will be in the range [1, 1000].
Each character S[i] will be in the set {'a', 'b', 'c', 'd'}.
Think
DP,三维数组dp[k, i, j]表示在s[i, j]内以字符k(‘a’ + k)为开头和结尾的回文串的数目,则有:
d p [ k , i , j ] = { 1 , i = j & s [ i ] = c h a r ( k ) 0 , i = j & s [ i ] ! = c h a r ( k ) d p [ k , i + 1 , j ] , s [ i ] ! = c h a r ( k ) & i < j d p [ k , i , j + 1 ] , s [ j ] ! = c h a r ( k ) & i < j 2 + d p [ 0 , i + 1 , j − 1 ] + d p [ 1 , i + 1 , j − 1 ] + d p [ 2 , i + 1 , j − 1 ] + d p [ 3 , i + 1 , j − 1 ] , s [ i ] = s [ j ] = c h a r ( k ) & i < j 0 , o t h e r w i s e dp[k, i, j]=\begin{cases}1,i=j\&s[i]=char(k)\\0,i=j\&s[i]!=char(k)\\dp[k, i+1, j],s[i]!=char(k)\&i<j\\dp[k, i, j+1],s[j]!=char(k)\&i<j\\2+dp[0,i+1,j-1]+dp[1,i+1,j-1]+dp[2,i+1,j-1]+dp[3,i+1,j-1],\\\ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ s[i]=s[j]=char(k)\&i<j\\0,otherwise\end{cases} d p [ k , i , j ] = ⎩ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎨ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎧ 1 , i = j & s [ i ] = c h a r ( k ) 0 , i = j & s [ i ] ! = c h a r ( k ) d p [ k , i + 1 , j ] , s [ i ] ! = c h a r ( k ) & i < j d p [ k , i , j + 1 ] , s [ j ] ! = c h a r ( k ) & i < j 2 + d p [ 0 , i + 1 , j − 1 ] + d p [ 1 , i + 1 , j − 1 ] + d p [ 2 , i + 1 , j − 1 ] + d p [ 3 , i + 1 , j − 1 ] , s [ i ] = s [ j ] = c h a r ( k ) & i < j 0 , o t h e r w i s e
这里第5种情况的2,表示当在dp[k, i + 1, j - 1]的外边框上加了字符char(k)之后,我们还需要额外添加c和cc这两个回文字符串(c = char(k))。
最后返回dp[k, 0, n - 1]在k=0-3上的总和。
Code
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 int countPalindromicSubsequences (string S) int n = S.size (); int mod = 1000000007 ; vector <vector <vector <int >>> dp (4 , vector <vector <int >>(n, vector <int >(n, 0 ))) for (int i = n - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--){ for (int j = i; j < n; j++){ for (int k = 0 ; k < 4 ; k++){ char c = 'a' + k; if (i == j){ if (S[i] == c) dp[k][i][j] = 1 ; else dp[k][i][j] = 0 ; } else if (S[i] != c){ dp[k][i][j] = dp[k][i + 1 ][j]; } else if (S[j] != c){ dp[k][i][j] = dp[k][i][j - 1 ]; } else { dp[k][i][j] = 2 ; for (int m = 0 ; m < 4 ; m++){ dp[k][i][j] += dp[m][i + 1 ][j - 1 ]; dp[k][i][j] %= mod; } } } } } int res = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < 4 ; i++){ res += dp[i][0 ][n - 1 ]; res %= mod; } return res; }
Review
回文串相关的题目解法比较多样化,主要有:
双指针,主要用于可以分别从左右两处进行比较的情况,如判断是否为回文串;
KMP算法中的部分匹配表的算法,主要用于计算可以和给定字符串构成最短回文串的字符串;
DFS或者backtracking,主要用于求具体有哪些回文串的情况,如分割字符串成多个回文串,需要状态上的回调;
DP,主要用于只需要求解个数的情况,一般dp[i, j]表示s[i, j]这个子字符串的情况,可以和双指针的思想结合使用,如求解分割字符串成多个回文串的方法个数;
中心扩展法,主要用于求解长度相关的问题,其高级版本为马拉车算法,如求解所有可能的回文子串;
贪心法,主要用于删除字符的问题;
分情况讨论,一般和上述方法结合使用。
P.S. 区分substring和subsequence,前者需要在原字符串内连续,后者不需要,但两者内部的顺序都和原字符串相符合。