LC1 Two Sum
Problem
Given a string, find the length of the longest substring without repeating characters.
Example 1:
2
3
Output: 3
Explanation: The answer is "abc", with the length of 3.Example 2:
2
3
Output: 1
Explanation: The answer is "b", with the length of 1.Example 3:
2
3
4
Output: 3
Explanation: The answer is "wke", with the length of 3.
Note that the answer must be a substring, "pwke" is a subsequence and not a substring.
Think
将数组改造成hashtable,然后遍历数组,找hashtable中是否有target - nums[i]
Code
1 | vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) { |
LC30 Substring with Concatenation of All Words
Problem
You are given a string, s, and a list of words, words, that are all of the same length. Find all starting indices of substring(s) in s that is a concatenation of each word in words exactly once and without any intervening characters.
Example 1:
2
3
4
5
6
s = "barfoothefoobarman",
words = ["foo","bar"]
Output: [0,9]
Explanation: Substrings starting at index 0 and 9 are "barfoo" and "foobar" respectively.
The output order does not matter, returning [9,0] is fine too.Example 2:
2
3
4
s = "wordgoodgoodgoodbestword",
words = ["word","good","best","word"]
Output: []
Think
首先将所有的words存在hash table中,计算所查找的子串的长度以及每个单词的长度和数量。
遍历开头长度为wordSize的子字符串,即第一个可能的起始节点在[0, wordSize - 1]中,设cnt为需要的word的数目。
然后遍历所有的word,如果word在map中存在,则对应的值-1,cnt - 1;如果此时j大于总共所需长度len = n * wordSize,则去找这个对应最开头的那一个长度为wordSize的子串,相当于滑动窗口的左端向右滑动了一位,使map中对应word+1, cnt+1;最后判断此时cnt是否等于0,如果等于0则说明找到一个满足条件的位置,
Code
1 | vector<int> findSubstring(string s, vector<string>& words) { |
LC36 Valid Sudoku
Problem
Determine if a 9x9 Sudoku board is valid. Only the filled cells need to be validated according to the following rules:
- Each row must contain the digits
1-9without repetition.- Each column must contain the digits
1-9without repetition.- Each of the 9
3x3sub-boxes of the grid must contain the digits1-9without repetition.
A partially filled sudoku which is valid.The Sudoku board could be partially filled, where empty cells are filled with the character
'.'.Example 1:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
[
["5","3",".",".","7",".",".",".","."],
["6",".",".","1","9","5",".",".","."],
[".","9","8",".",".",".",".","6","."],
["8",".",".",".","6",".",".",".","3"],
["4",".",".","8",".","3",".",".","1"],
["7",".",".",".","2",".",".",".","6"],
[".","6",".",".",".",".","2","8","."],
[".",".",".","4","1","9",".",".","5"],
[".",".",".",".","8",".",".","7","9"]
]
Output: trueExample 2:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
[
["8","3",".",".","7",".",".",".","."],
["6",".",".","1","9","5",".",".","."],
[".","9","8",".",".",".",".","6","."],
["8",".",".",".","6",".",".",".","3"],
["4",".",".","8",".","3",".",".","1"],
["7",".",".",".","2",".",".",".","6"],
[".","6",".",".",".",".","2","8","."],
[".",".",".","4","1","9",".",".","5"],
[".",".",".",".","8",".",".","7","9"]
]
Output: false
Explanation: Same as Example 1, except with the 5 in the top left corner being
modified to 8. Since there are two 8's in the top left 3x3 sub-box, it is invalid.Note:
- A Sudoku board (partially filled) could be valid but is not necessarily solvable.
- Only the filled cells need to be validated according to the mentioned rules.
- The given board contain only digits
1-9and the character'.'.- The given board size is always
9x9.
Think
直接判断每行每列和每个3x3矩阵即可
Code
1 | bool isValidSudoku(vector<vector<char>>& board) { |
LC37 Sudoku Solver
Problem
Write a program to solve a Sudoku puzzle by filling the empty cells.
A sudoku solution must satisfy all of the following rules:
- Each of the digits
1-9must occur exactly once in each row.- Each of the digits
1-9must occur exactly once in each column.- Each of the the digits
1-9must occur exactly once in each of the 93x3sub-boxes of the grid.Empty cells are indicated by the character
'.'.
A sudoku puzzle…
…and its solution numbers marked in red.Note:
- The given board contain only digits
1-9and the character'.'.- You may assume that the given Sudoku puzzle will have a single unique solution.
- The given board size is always
9x9.
Think
回溯递归,判断当前填写是否合法
Code
1 | void solveSudoku(vector<vector<char>>& board) { |
LC76 Minimum Window Substring
Problem
Given a string S and a string T, find the minimum window in S which will contain all the characters in T in complexity O(n).
Example:
2
Output: "BANC"Note:
- If there is no such window in S that covers all characters in T, return the empty string
"".- If there is such window, you are guaranteed that there will always be only one unique minimum window in S.
Think
hash table + 滑动窗口
首先将t中所有的字母都存在hash table中,然后预处理字符串s,删去其中所有的不存在于t中的字符,转化为包含下标和字符的数组;
设置滑动窗口为[l, r],判断r处的字符是否在t中,且是否有剩余的容量,如果恰好容量到达t中该字符的数目,则已匹配好的字符数目formed ++;然后对左端的l进行右移处理:如果formed == required,则可以右移l,并将当前的[l, r]存进结果中,然后将l处的字符的数目恢复即可。
Code
1 | string minWindow(string s, string t) { |
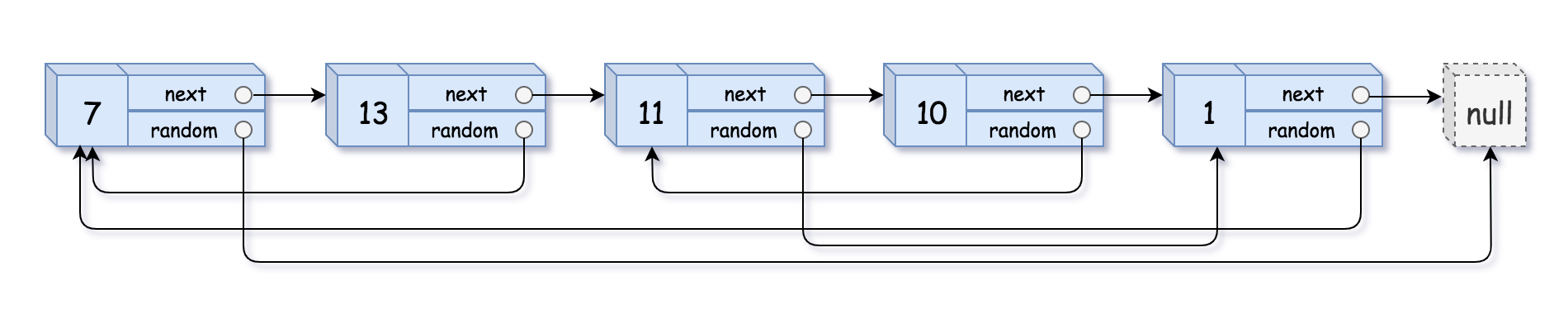
LC138 Copy List with Random Pointer
Problem
A linked list is given such that each node contains an additional random pointer which could point to any node in the list or null.
Return a deep copy of the list.
The Linked List is represented in the input/output as a list of
nnodes. Each node is represented as a pair of[val, random_index]where:
val: an integer representingNode.valrandom_index: the index of the node (range from0ton-1) where random pointer points to, ornullif it does not point to any node.Example 1:
2
Output: [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]Example 2:
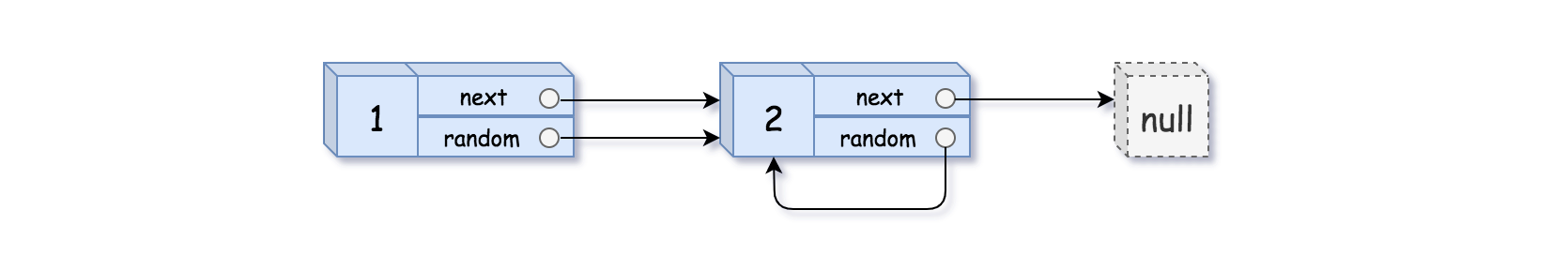
2
Output: [[1,1],[2,1]]Example 3:
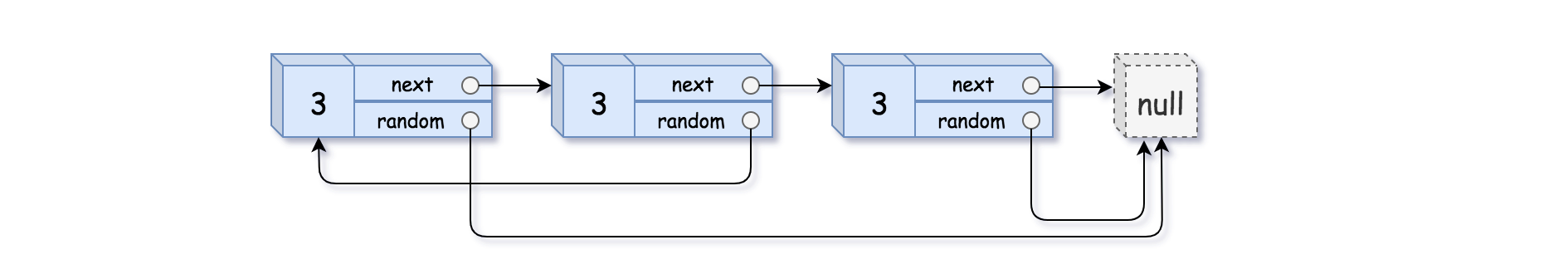
2
Output: [[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]]Example 4:
2
3
Output: []
Explanation: Given linked list is empty (null pointer), so return null.Constraints:
-10000 <= Node.val <= 10000Node.randomis null or pointing to a node in the linked list.- Number of Nodes will not exceed 1000.
Think
- Approach 1
递归+hash table
- Approach 2
三次遍历,第一次复制节点,插在当前节点之后;第二次赋值random指针;第三次断开链接,注意要恢复原来的链表。
Code
- Approach 1
1 | Node* copyRandomList(Node* head) { |
- Approach 2
1 | Node* copyRandomList(Node* head) { |
LC149 Max Points on a Line
Problem
Given n points on a 2D plane, find the maximum number of points that lie on the same straight line.
Example 1:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Output: 3
Explanation:
^
|
| o
| o
| o
+------------->
0 1 2 3 4Example 2:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
Output: 4
Explanation:
^
|
| o
| o o
| o
| o o
+------------------->
0 1 2 3 4 5 6NOTE: input types have been changed on April 15, 2019. Please reset to default code definition to get new method signature.
Think
分三部分,首先确定一个点,然后判断和这个点在一条直线上的点的数目(未遍历过的点),其中分解为对于每一个点,都将这个点和初始选择的点构成的直线加入到map中,注意此处需要判断重复点和水平线(或者竖直线)的情况。
p.s.由于double可能存在精度不够的情况,这里采用pair<dx, dy>作为map的key,因此需要先进行化简,即先求最小公约数。
Code
1 | vector<vector<int>> points; |
LC166 Fraction to Recurring Decimal
Problem
Given two integers representing the numerator and denominator of a fraction, return the fraction in string format.
If the fractional part is repeating, enclose the repeating part in parentheses.
Example 1:
2
Output: "0.5"Example 2:
2
Output: "2"Example 3:
2
Output: "0.(6)"
Think
首先判断结果的正负,然后将除数和被除数都转变为long型的正数,求出整数部分和余数remainder。
如果remainder = 0,说明为整数,直接返回即可;
如果remainder不为0,则建立一个hash table,存放每一个remainder对应在res的什么位置;当remainder不等于0时循环:如果此时hash table中存在当前remainder,说明之前遇到过这个remainder,也就是产生了循环,因此直接去hash table中找上一次遇到这个remainder的开始的位置,在那个地方插入左括号,res最右端插入右括号,返回即可;否则,记录当前remainder的位置,remainder乘10,然后将这一位的结果存入res,remainder变成这一位除完的余数。
Code
1 | string fractionToDecimal(int numerator, int denominator) { |
LC187 Repeated DNA Sequences
Problem
All DNA is composed of a series of nucleotides abbreviated as A, C, G, and T, for example: “ACGAATTCCG”. When studying DNA, it is sometimes useful to identify repeated sequences within the DNA.
Write a function to find all the 10-letter-long sequences (substrings) that occur more than once in a DNA molecule.
Example:
2
3
Output: ["AAAAACCCCC", "CCCCCAAAAA"]
Think
滑动窗口+hash table,注意substr的复杂度为O(L),其中L为截取的长度。
Code
1 | vector<string> findRepeatedDnaSequences(string s) { |
LC204 Count Primes
Problem
Count the number of prime numbers less than a non-negative number, *n*.
Example:
2
3
Output: 4
Explanation: There are 4 prime numbers less than 10, they are 2, 3, 5, 7.
Think
设定一个长度为n的数组,每一位表示当前下标对应的数字处是否为质数。遍历数组,如果当前数字为质数,则将所有它的倍数都置为true。统计这个数组中false的数目即可。
Code
1 | int countPrimes(int n) { |
LC205 Isomorphic Strings
Problem
Given two strings *s* and *t*, determine if they are isomorphic.
Two strings are isomorphic if the characters in *s* can be replaced to get *t*.
All occurrences of a character must be replaced with another character while preserving the order of characters. No two characters may map to the same character but a character may map to itself.
Example 1:
2
Output: trueExample 2:
2
Output: falseExample 3:
2
Output: trueNote:
You may assume both *s* and *t* have the same length.
Think
首先建立数组m1和m2,其包含了s和t里面的每个字符串和下标的对应关系。如果当前字符串s在m1中对应的下标和字符串t在m2中对应的下标不一致,则说明这当中某一个字符出现在了别的地方,也就是不满足要求的一一对应的关系,返回false,否则记录当前的字符和下标。
Code
1 | bool isIsomorphic(string s, string t) { |
LC217 Contains Duplicate
Problem
Given an array of integers, find if the array contains any duplicates.
Your function should return true if any value appears at least twice in the array, and it should return false if every element is distinct.
Example 1:
2
Output: trueExample 2:
2
Output: falseExample 3:
2
Output: true
Think
hash table
Code
1 | bool containsDuplicate(vector<int>& nums) { |
LC219 Contains Duplicate II
Problem
Given an array of integers and an integer k, find out whether there are two distinct indices i and j in the array such that nums[i] = nums[j] and the absolute difference between i and j is at most k.
Example 1:
2
Output: trueExample 2:
2
Output: trueExample 3:
2
Output: false
Think
Hash table存放当前数字和下标
Code
1 | bool containsNearbyDuplicate(vector<int>& nums, int k) { |
LC242 Valid Anagram
Problem
Given two strings s and t , write a function to determine if t is an anagram of s.
Example 1:
2
Output: trueExample 2:
2
Output: falseNote:
You may assume the string contains only lowercase alphabets.Follow up:
What if the inputs contain unicode characters? How would you adapt your solution to such case?
Think
Hash table,分别遍历s和t,判断是否还有余量
Code
1 | bool isAnagram(string s, string t) { |
LC274 H-Index
Problem
Given an array of citations (each citation is a non-negative integer) of a researcher, write a function to compute the researcher’s h-index.
According to the definition of h-index on Wikipedia: “A scientist has index h if h of his/her Npapers have at least h citations each, and the other N − h papers have no more than hcitations each.”
Example:
2
3
4
5
6
Output: 3
Explanation: [3,0,6,1,5] means the researcher has 5 papers in total and each of them had
received 3, 0, 6, 1, 5 citations respectively.
Since the researcher has 3 papers with at least 3 citations each and the remaining
two with no more than 3 citations each, her h-index is 3.Note: If there are several possible values for h, the maximum one is taken as the h-index.
Think
首先对论文进行升序排序,设当前遍历到的论文为i,则每次判断第n - 1 - i篇论文(即第i大的论文)的引用数是否大于i,如果大于,则说明要找的临界点还在后面,i++,否则返回i即可。
Code
1 | int hIndex(vector<int>& citations) { |