LC5 Longest Palindromic Substring
Problem
Given a string s, find the longest palindromic substring in s. You may assume that the maximum length of s is 1000.
Example 1:
Input: “babad”
Output: “bab”
Note: “aba” is also a valid answer.Example 2:
Input: “cbbd”
Output: “bb”
Think
- Approach 1
Use two dimension dp vector and dp[i, j] denotes if s[i…j] is palindromic string. When s[i…j] is palindromic substring, dp[i, j] = true, otherwise dp[i, j] = false.
Initial conditions are: dp[i, i] = true; when s[i] == s[i + 1], dp[i, i + 1] = true, otherwise false.
dp[i, j] = dp[i + 1, j - 1] && s[i] == s[j]
- Approach 2
Expand around center. A palindromic string mirrors around its center. Such a string s could have 2n - 1 center.
- Approach 3
马拉车算法
首先做预处理,在每一个间隔处加上#,开头加上$符号如
noon -> $#n#o#o#n#
这样处理过后的字符串的长度一定是奇数,设为字符串t。设p[i]表示以t[i]为中心的最长回文串的半径,则原字符串s中以t[i]字符为中心的最长回文串的长度为p[i] - 1,该回文串在s中的起始位置为(i - p[i]) / 2。
计算p[i]数组,两个辅助变量:mx表示回文串能延伸到的最右边的位置,id为mx对应的回文串的中心点位置
1 | p[i] = mx > i ? min(p[2 * id - i], mx - i) : 1; |
Code
- Approach 1
1 | string longestPalindrome(string s) { |
- Approach 2
1 | string longestPalindrome(string s) { |
- Approach 3
1 | string longestPalindrome(string s) { |
LC10 Regular Expression Matching
Problem
Given an input string (
s) and a pattern (p), implement regular expression matching with support for'.'and'*'.
2
'*' Matches zero or more of the preceding element.The matching should cover the entire input string (not partial).
Note:
scould be empty and contains only lowercase lettersa-z.pcould be empty and contains only lowercase lettersa-z, and characters like.or*.Example 1:
2
3
4
5
s = "aa"
p = "a"
Output: false
Explanation: "a" does not match the entire string "aa".Example 2:
2
3
4
5
s = "aa"
p = "a*"
Output: true
Explanation: '*' means zero or more of the preceding element, 'a'. Therefore, by repeating 'a' once, it becomes "aa".Example 3:
2
3
4
5
s = "ab"
p = ".*"
Output: true
Explanation: ".*" means "zero or more (*) of any character (.)".Example 4:
2
3
4
5
s = "aab"
p = "c*a*b"
Output: true
Explanation: c can be repeated 0 times, a can be repeated 1 time. Therefore, it matches "aab".Example 5:
2
3
4
s = "mississippi"
p = "mis*is*p*."
Output: false
Think
- Approach 1
递归
若p为空,判断s是否为空,s为空则返回true,否则返回false;
判断s和p的第一个字符是否匹配,即s不为空,且s[0] == p[0] || p[0] == '.'时匹配成功;
若p的长度大于等于2,且第二个字符为*,则判断s和p[2:]是否匹配,或者在第一个字符匹配的情况下判断s[1:]和p是否匹配;
否则判断在第一个字符匹配的情况下s[1:]和p[1:]是否匹配。
- Approach 2
DP
dp[i, j]表示判断s[i:]和p[j:]是否匹配
在求dp[i, j]时,首先判断s[i]和p[j]是否匹配,设值为first_match;
若j+1位在p的范围内,且p[j+1] == ‘*’,则dp[i, j] = dp[i, j + 2] || (first_match && dp[i + 1, j]);
否则,dp[i, j] = first_match && dp[i + 1, j + 1];
Code
- Approach 1
1 | bool isMatch(string s, string p) { |
- Approach 2
1 | bool isMatch(string s, string p) { |
LC32 Longest Valid Parentheses
Problem
Given a string containing just the characters
'('and')', find the length of the longest valid (well-formed) parentheses substring.Example 1:
2
3
Output: 2
Explanation: The longest valid parentheses substring is "()"Example 2:
2
3
Output: 4
Explanation: The longest valid parentheses substring is "()()"
Think
- Approach 1
DP,以右括号为基准进行判断,dp[i]表示以s[i]为结尾的最长的符合要求的字符串的长度;
当s[i] == ')'时:
若s[i - 1] == ‘(’,dp[i] = dp[i - 2] + 2;
若s[i - 1] == ‘)’,若s[i - dp[i - 1] - 1] == ‘(’,则dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + dp[i - dp[i - 1] - 2] + 2;
- Approach 2
stack,初始放入-1,读到左括号时将下标放入stack中;
读到右括号时pop栈顶元素:
若此时栈为空,则将当前下标放入栈中,表示当前可匹配的最前字符;
否则求i - stack.top()和maxLen的大小关系
- Approach 3
分别从左右两边遍历字符串,设left = right = 0;
左遍历:当读到左括号的时候left++,读到右括号的时候right++;若left=right说明可以匹配,求最大值;若left<right说明左括号不够匹配右括号,则将left和right归零;
右遍历:当读到左括号的时候left++,读到右括号的时候right++;若left=right说明可以匹配,求最大值;若left>right说明右括号不够匹配左括号,则将left和right归零;
Code
- Approach 1
1 | int longestValidParentheses(string s) { |
- Approach 2
1 | int longestValidParentheses(string s) { |
- Approach 3
1 | int longestValidParentheses(string s) { |
LC44 Wildcard Matching
Problem
Given an input string (
s) and a pattern (p), implement wildcard pattern matching with support for'?'and'*'.
2
'*' Matches any sequence of characters (including the empty sequence).The matching should cover the entire input string (not partial).
Note:
scould be empty and contains only lowercase lettersa-z.pcould be empty and contains only lowercase lettersa-z, and characters like?or*.Example 1:
2
3
4
5
s = "aa"
p = "a"
Output: false
Explanation: "a" does not match the entire string "aa".Example 2:
2
3
4
5
s = "aa"
p = "*"
Output: true
Explanation: '*' matches any sequence.Example 3:
2
3
4
5
s = "cb"
p = "?a"
Output: false
Explanation: '?' matches 'c', but the second letter is 'a', which does not match 'b'.Example 4:
2
3
4
5
s = "adceb"
p = "*a*b"
Output: true
Explanation: The first '*' matches the empty sequence, while the second '*' matches the substring "dce".Example 5:
2
3
4
s = "acdcb"
p = "a*c?b"
Output: false
Think
DP,设dp[i, j]为s的前i个字符和p的前j个字符的匹配结果,则有
若s[i]和p[j]匹配,则dp[i, j] = dp[i - 1, j - 1];
否则若p[j] == ‘*’,则dp[i, j] = dp[i - 1, j - 1] || dp[i - 1, j] || dp[i, j - 1];
否则dp[i, j] = false;
初始条件:
s和p均为空的时候,dp[0, 0] = true;
s为空,p必须全部为’*’,dp[0, i]= dp[0, i - 1] && p[i - 1] == ‘*’;
p为空的时候,dp[i, 0] = false;
Code
1 | bool isMatch(string s, string p) { |
LC62 Unique Paths
Problem
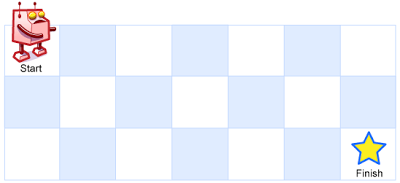
A robot is located at the top-left corner of a m x n grid (marked ‘Start’ in the diagram below).
The robot can only move either down or right at any point in time. The robot is trying to reach the bottom-right corner of the grid (marked ‘Finish’ in the diagram below).
How many possible unique paths are there?
Above is a 7 x 3 grid. How many possible unique paths are there?Example 1:
2
3
4
5
6
7
Output: 3
Explanation:
From the top-left corner, there are a total of 3 ways to reach the bottom-right corner:
1. Right -> Right -> Down
2. Right -> Down -> Right
3. Down -> Right -> RightExample 2:
2
Output: 28
Think
DP,dp[i, j] = dp[i - 1, j] + dp[i, j - 1];初始情况:dp[0, i] = dp[j, 0] = 1
可以转成一维数组:dp[i]表示一行的情况,dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + dp[i];
Code
1 | int uniquePaths(int m, int n) { |
LC63 Unique Paths II
Problem
A robot is located at the top-left corner of a m x n grid (marked ‘Start’ in the diagram below).
The robot can only move either down or right at any point in time. The robot is trying to reach the bottom-right corner of the grid (marked ‘Finish’ in the diagram below).
Now consider if some obstacles are added to the grids. How many unique paths would there be?
An obstacle and empty space is marked as
1and0respectively in the grid.Note: m and n will be at most 100.
Example 1:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
[
[0,0,0],
[0,1,0],
[0,0,0]
]
Output: 2
>Explanation:
There is one obstacle in the middle of the 3x3 grid above.
>There are two ways to reach the bottom-right corner:
1. Right -> Right -> Down -> Down
2. Down -> Down -> Right -> Right
Think
类似LC62的做法,使用二维DP即可Code
1 | int uniquePathsWithObstacles(vector<vector<int>>& obstacleGrid) { |
Review
- DP问题最大的特点:最优子结构,所以当发现某一个问题是具有一定的递归性的,可以考虑用DP解决
- 在确定DP的递推公式的时候,第一要尝试对当前状态的相邻状态的递推转化,第二要尝试对可以从当前状态到达的状态或者可以到达当前状态的状态进行转化
- 注意边界条件,一般是某一个维度为0的时候